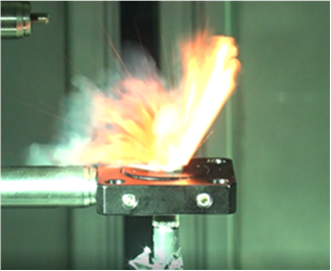
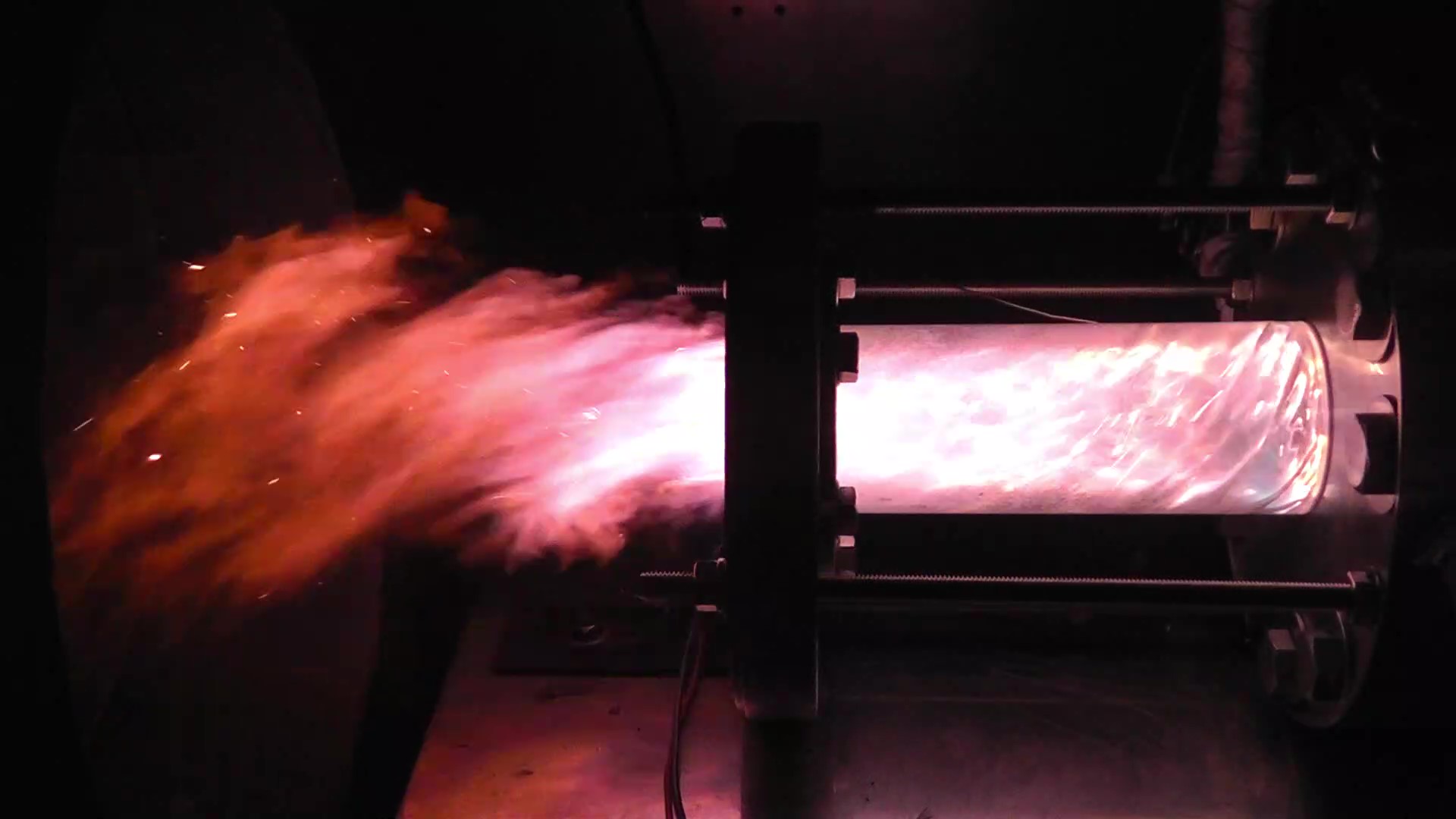
What is Laser Ignition?
Laser ignition is a new ignition method for rocket engines that has become feasible with the development of compact semiconductor lasers. Ignition is achieved by directly irradiating the igniter material with a laser.
Conventional methods using heated wires require the rocket to be equipped with a safety device to prevent electrical disturbances. In contrast, laser ignition systems are unaffected by such disturbances, eliminating the need to install these safety devices on the rocket.
As a result, the freed internal volume can be used for additional propellant, improving the rocket’s overall performance. At the same time, removing the safety system also reduces costs.
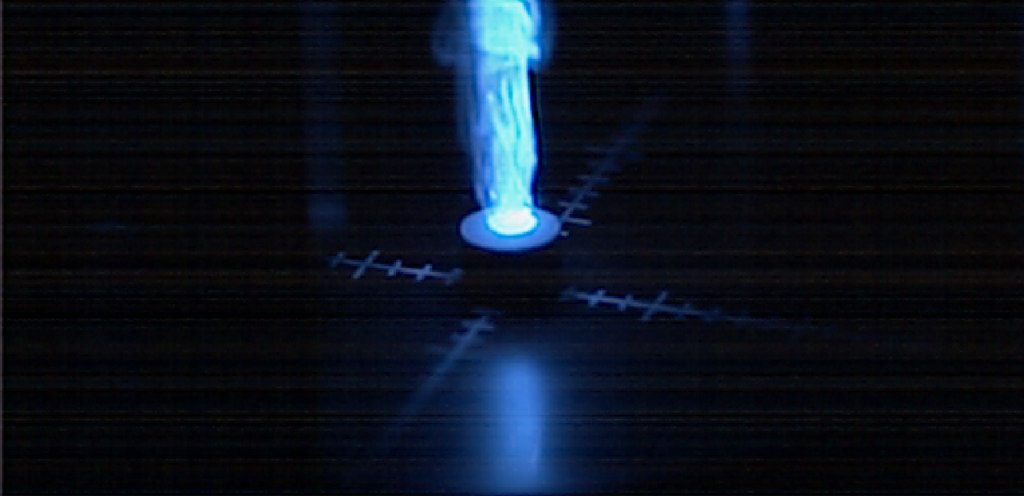

Research
Currently, Laser ignition devices are being considered as an ignition method for solid rocket motors in space. Space is a near-vacuum environment at temperatures roughly around 3 Kelvin, and spacecraft become very cold through radiative heat loss and are continuously exposed to near-vacuum conditions.
To implement laser-ignited solid motors, the reliability of the laser ignition system under low-temperature and vacuum conditions must be evaluated.
Therefore, our laboratory is conducting research to clarify the ignition characteristics of the igniter material when irradiated by a laser under low-temperature and vacuum conditions.